Thigh
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2011) |
| Thigh | |
|---|---|
 Front and medial aspect of a male right thigh | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | femur |
| MeSH | D013848 |
| TA98 | A01.1.00.035 |
| TA2 | 160 |
| FMA | 24967 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In humans the thigh is the area between the pelvis and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.[1]
The single bone in the thigh is called the femur. This bone is very thick and strong (due to the high proportion of cortical bone), and forms a ball and socket joint at the hip, and a condylar joint at the knee.
Fascial compartments
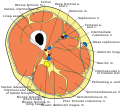
In cross-section, the thigh is divided up into three fascial compartments. These compartments use the femur as an axis, and are separated by tough connective tissue membranes (or septa). Each of these compartments has its own blood and nerve supply, and contains a different group of muscles.
- Medial fascial compartment of thigh, adductor
- Posterior fascial compartment of thigh, flexor, hamstring
- Anterior fascial compartment of thigh, extensor
Overall, the leg (lower limb) consists of seven interior bones:
Blood vessels
The arterial supply is by the femoral artery and the obturator artery. The lymphatic drainage closely follows the arterial supply and drains to the lumbar lymphatic trunks on the corresponding side, which in turn drains to the cisterna chyli.
The deep venous system of the thigh consists of the femoral vein, the proximal part of the popliteal vein, and various smaller vessels; these are the site of proximal deep venous thrombosis. The venae perfortantes connect the deep and the superficial system, which consists of the saphenous veins (the site of varicose veins).
Thigh weakness
Thigh weakness can result in a positive Gowers' sign on physical examination.
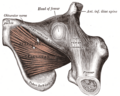
Muscles and Fascia of the Thigh
Anterior compartment muscles of the thigh include pectineus, sartorius, and the four muscles that comprise the quadriceps muscles- rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius and vastus lateralis.
Posterior compartment muscles of the thigh are the hamstring muscles, which include semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris.
Medial compartment muscles are adductor magnus, adductor longus and adductor brevis, and also gracilis.
-
Front of thigh muscles from Gray's Anatomy of the human body from 1918.
-
Back thigh muscles of the gluteal and posterior femoral regions from Gray's Anatomy of the human body from 1918.
-
Cross-section through the middle of the thigh.
-
Cross-section through the middle of the thigh.