„Fox H-Funktion“ – Versionsunterschied
| [gesichtete Version] | [gesichtete Version] |
K Gripweed verschob die Seite Benutzer:Versionen/Fox H-function nach Fox H-Funktion, ohne dabei eine Weiterleitung anzulegen: Versionsimport |
K Revert auf Version von Benutzer:M2k~dewiki (1. Mär. 2023, 23:57). Grund: zurück Markierung: Manuelle Zurücksetzung |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
In der Mathematik ist die '''Fox H-Funktion''' ''H''(''x'') eine Verallgemeinerung der [[Meijersche G-Funktion|Meijer G-Funktion]] und der Fox–Wright Funktion, eingeführt von [[Charles Fox (Mathematiker)|Charles Fox]] (1961). |
|||
{{Short description|Generalization of the Meijer G-function and the Fox–Wright function}} |
|||
Die die Definition ist gegeben durch ein Mellin–Barnes-Integral |
|||
{{Redirect-distinguish|H function|Harmonic number}} |
|||
In mathematics, the '''Fox H-function''' ''H''(''x'') is a generalization of the [[Meijer G-function]] and the [[Fox–Wright function]] introduced by {{harvs|txt|authorlink=Charles Fox (mathematician)|first=Charles|last=Fox|year=1961}}. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
It is defined by a [[Mellin–Barnes integral]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
H_{p,q}^{\,m,n} \!\left[ z \left| \begin{matrix} |
H_{p,q}^{\,m,n} \!\left[ z \left| \begin{matrix} |
||
( a_1 , A_1 ) & ( a_2 , A_2 ) & \ldots & ( a_p , A_p ) \\ |
( a_1 , A_1 ) & ( a_2 , A_2 ) & \ldots & ( a_p , A_p ) \\ |
||
| Zeile 13: | Zeile 12: | ||
z^{-s} \, ds, |
z^{-s} \, ds, |
||
</math> |
</math> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
wobei L ein bestimmter Weg ist, die die Pole der beiden Faktoren im Zähler trennt. |
|||
== Relation to other Functions == |
|||
| ⚫ | [[Datei:Plot_of_the_Fox_H_function_H((((a_1,α_1),...,(a_n,α_n)),((a_n+1,α_n+1),...,(a_p,α_p)),(((b_1,β_1),...,(b_m,β_m)),in_((b_m+1,β_m+1),...,(b_q,β_q))),z)_with_H(((),()),(((-1,½)),()),z).svg|alternativtext=Plot of the Fox H function H((((a 1,α 1),...,(a n,α n)),((a n+1,α n+1),...,(a p,α p)),(((b 1,β 1),...,(b m,β m)),in ((b m+1,β m+1),...,(b q,β q))),z) with H(((),()),(((-1,½)),()),z)|mini|Plot of the Fox H function H((((a 1,α 1),...,(a n,α n)),((a n+1,α n+1),...,(a p,α p)),(((b 1,β 1),...,(b m,β m)),in ((b m+1,β m+1),...,(b q,β q))),z) with H(((),()),(((-1,½)),()),z)]] |
||
== Beziehung zu anderen Funktionen == |
|||
=== Lambert W-function === |
|||
A relation of the Fox H-Function to the -1 branch of the [[Lambert W function|Lambert W-function]] is given by |
|||
=== Lambertsche W-Funktion === |
|||
Eine Relation der Fox H-Funktion zu den Zweig -1 der [[Lambertsche W-Funktion|Lambertschen W-Funktion]] ist gegeben durch |
|||
<math> |
<math> |
||
\overline{\operatorname{W}_{-1}\left( -\alpha \cdot z \right)} = \begin{cases} \lim_{\beta \to \alpha^{-}} \left[ \frac{\alpha^{2} \cdot \left( \left( \alpha - \beta \right) \cdot z \right)^{\frac{\alpha}{\beta}}}{\beta} \cdot \operatorname{H}_{1,\, 2}^{1,\, 1} \left( \begin{matrix} \left( \frac{\alpha + \beta}{\beta},\, \frac{\alpha}{\beta} \right)\\ \left( 0,\, 1 \right),\, \left( -\frac{\alpha}{\beta},\, \frac{\alpha - \beta}{\beta} \right)\\\end{matrix} \mid -\left( \left( \alpha - \beta \right) \cdot z \right)^{\frac{\alpha}{\beta} - 1} \right) \right],\, \text{ |
\overline{\operatorname{W}_{-1}\left( -\alpha \cdot z \right)} = \begin{cases} \lim_{\beta \to \alpha^{-}} \left[ \frac{\alpha^{2} \cdot \left( \left( \alpha - \beta \right) \cdot z \right)^{\frac{\alpha}{\beta}}}{\beta} \cdot \operatorname{H}_{1,\, 2}^{1,\, 1} \left( \begin{matrix} \left( \frac{\alpha + \beta}{\beta},\, \frac{\alpha}{\beta} \right)\\ \left( 0,\, 1 \right),\, \left( -\frac{\alpha}{\beta},\, \frac{\alpha - \beta}{\beta} \right)\\\end{matrix} \mid -\left( \left( \alpha - \beta \right) \cdot z \right)^{\frac{\alpha}{\beta} - 1} \right) \right],\, \text{falls} \left| |
||
z \right| < \frac{1}{e \left| \alpha \right|}\\ |
z \right| < \frac{1}{e \left| \alpha \right|}\\ |
||
\lim_{\beta \to \alpha^{-}} \left[ \frac{\alpha^{2} \cdot \left( \left( \alpha - \beta \right) \cdot z \right)^{-\frac{\alpha}{\beta}}}{\beta} \cdot \operatorname{H}_{2,\, 1}^{1,\, 1} \left( \begin{matrix} \left( 1,\, 1 \right),\, \left( \frac{\beta - \alpha}{\beta},\, \frac{\alpha - \beta}{\beta} \right)\\ \left( -\frac{\alpha}{\beta},\, \frac{\alpha}{\beta} \right)\\\end{matrix} \mid -\left( \left( \alpha - \beta \right) \cdot z \right)^{1 - \frac{\alpha}{\beta}} \right) \right],\, \text{ |
\lim_{\beta \to \alpha^{-}} \left[ \frac{\alpha^{2} \cdot \left( \left( \alpha - \beta \right) \cdot z \right)^{-\frac{\alpha}{\beta}}}{\beta} \cdot \operatorname{H}_{2,\, 1}^{1,\, 1} \left( \begin{matrix} \left( 1,\, 1 \right),\, \left( \frac{\beta - \alpha}{\beta},\, \frac{\alpha - \beta}{\beta} \right)\\ \left( -\frac{\alpha}{\beta},\, \frac{\alpha}{\beta} \right)\\\end{matrix} \mid -\left( \left( \alpha - \beta \right) \cdot z \right)^{1 - \frac{\alpha}{\beta}} \right) \right],\, \text{andernfalls}\\ \end{cases} |
||
</math> |
</math>wobei <math> |
||
\overline{z} |
\overline{z} |
||
</math> |
</math> das komplex-konjugierte <math> |
||
z |
z |
||
</math>.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Rathie and Ozelim |first=Pushpa Narayan and Luan Carlos de Sena Monteiro |title=On the Relation between Lambert W-Function and Generalized |
</math> ist.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Rathie and Ozelim |first=Pushpa Narayan and Luan Carlos de Sena Monteiro |title=On the Relation between Lambert W-Function and Generalized |
||
Hypergeometric Functions |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365706509_On_the_Relation_between_Lambert_W-Function_and_Generalized_Hypergeometric_Functions | |
Hypergeometric Functions |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365706509_On_the_Relation_between_Lambert_W-Function_and_Generalized_Hypergeometric_Functions |accessdate=01.03.2023 |website=Researchgate}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Vergleich zur Meijer G-Funktion |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Compare to the Meijer G-function |
|||
: |
: |
||
<math> |
<math> |
||
G_{p,q}^{\,m,n} \!\left( \left. \begin{matrix} a_1, \dots, a_p \\ b_1, \dots, b_q \end{matrix} \; \right| \, z \right) = \frac{1}{2 \pi i} \int_L |
G_{p,q}^{\,m,n} \!\left( \left. \begin{matrix} a_1, \dots, a_p \\ b_1, \dots, b_q \end{matrix} \; \right| \, z \right) = \frac{1}{2 \pi i} \int_L |
||
| Zeile 41: | Zeile 44: | ||
</math> |
</math> |
||
Der Spezialfall für welchen die Fox H-Funktion zur Meijer G-Funktion reduziert wird ist bei ''A''<sub>''j''</sub> = ''B''<sub>''k''</sub> = ''C'', ''C'' > 0 für ''j'' = 1...''p'' und ''k'' = 1...''q'' |
|||
:<math> |
: <math> |
||
H_{p,q}^{\,m,n} \!\left[ z \left| \begin{matrix} |
H_{p,q}^{\,m,n} \!\left[ z \left| \begin{matrix} |
||
( a_1 , C ) & ( a_2 , C ) & \ldots & ( a_p , C ) \\ |
( a_1 , C ) & ( a_2 , C ) & \ldots & ( a_p , C ) \\ |
||
| Zeile 50: | Zeile 54: | ||
</math> |
</math> |
||
Eine Verallgemeinerung der Fox H-Funktion ist geben von Ram Kishore Saxena<ref>{{Literatur |ISBN=978-0-387-06482-6 |sprache=en}}</ref> und Innayat Hussain AA (1987). Für eine weitere Verallgemeinerung, welche sich in der Physik und Statistik als nützlich erweisen wie A.M.Mathai und Ram Kishore Saxena zeigten,<ref>{{Literatur |ISBN=978-0-470-26380-8 |sprache=en}}</ref> siehe Rathie (1997). |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
*{{Citation | last1= Fox | first1= Charles | title= The G and H functions as symmetrical Fourier kernels | jstor= 1993339 | mr= 0131578 | year= 1961 | journal= [[Transactions of the American Mathematical Society]] | issn= 0002-9947 | volume= 98 | issue= 3 | pages= 395–429 | doi=10.2307/1993339}} |
|||
*{{Citation | last= Innayat-Hussain | first=AA | title= New properties of hypergeometric series derivable from Feynman integrals. I: Transformation and reduction formulae | journal= J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. | volume= 20 | year= 1987 | pages= 4109–4117 | doi= 10.1088/0305-4470/20/13/019 }} |
|||
*{{Citation | last= Innayat-Hussain | first=AA | title= New properties of hypergeometric series derivable from Feynman integrals. II: A generalization of the H-function | journal= J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. | volume= 20 | year= 1987 | issue=13 | pages= 4119–4128 | doi= 10.1088/0305-4470/20/13/020 }} |
|||
*{{Citation |
|||
| last1= Kilbas | first1= Anatoly A. |
|||
| title=H-Transforms: Theory and Applications |
|||
| publisher= CRC Press |
|||
| isbn= 978-0415299169 |
|||
| year= 2004 }} |
|||
*{{Citation | last1= Mathai | first1= A. M. | last2=Saxena | first2=Ram Kishore | title= The H-function with applications in statistics and other disciplines | publisher= Halsted Press [John Wiley & Sons], New York-London-Sidney | isbn= 978-0-470-26380-8 | mr=513025 | year= 1978 }} |
|||
*{{Citation | last1= Mathai | first1= A. M. | last2= Saxena | first2= Ram Kishore | last3= Haubold | first3= Hans J. | title= The H-function | publisher= [[Springer-Verlag]] | location= Berlin, New York | isbn= 978-1-4419-0915-2 | mr= 2562766 | year= 2010 }} |
|||
*{{Citation | last= Rathie | first= Arjun K. | title= A new generalization of generalized hypergeometric function | journal= Le Matematiche | volume= LII | year= 1997 | pages= 297–310 }}. |
|||
*{{Citation | last1= Srivastava | first1= H. M. | last2= Gupta | first2= K. C. | last3= Goyal | first3= S. P. | title= The H-functions of one and two variables | publisher= South Asian Publishers Pvt. Ltd. | location= New Delhi | mr= 691138 | year= 1982 }} |
|||
* {{cite book | last1= Srivastava | first1= H. M. | last2= Manocha | first2= H. L. | title= A treatise on generating functions | year= 1984 | isbn= 0-470-20010-3 }} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
* [https://gitlab.com/RZ-FZJ/hypergeom hypergeom] on [[GitLab]] |
|||
* [https://mathoverflow.net/questions/407760/is-there-a-specific-named-function-that-is-the-inverse-of-xxa-for-x-real/407777#407777 Use in solving <math>x+x^a=y</math>] on [[MathOverflow]] |
|||
[[Category:Hypergeometric functions]] |
|||
[[Category:Special functions]] |
|||
== Einzelnachweise == |
|||
{{mathanalysis-stub}} |
|||
<references></references> |
|||
{{SORTIERUNG:Fox HFunktion}} |
|||
[[Kategorie:Funktionentheorie]] |
|||
[[Kategorie:Analytische Funktion]] |
|||
Version vom 2. März 2023, 01:15 Uhr
In der Mathematik ist die Fox H-Funktion H(x) eine Verallgemeinerung der Meijer G-Funktion und der Fox–Wright Funktion, eingeführt von Charles Fox (1961). Die die Definition ist gegeben durch ein Mellin–Barnes-Integral
wobei L ein bestimmter Weg ist, die die Pole der beiden Faktoren im Zähler trennt.
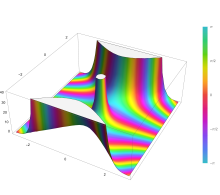
Beziehung zu anderen Funktionen
Lambertsche W-Funktion
Eine Relation der Fox H-Funktion zu den Zweig -1 der Lambertschen W-Funktion ist gegeben durch
wobei das komplex-konjugierte ist.[1]
Meijer G-Funktion
Vergleich zur Meijer G-Funktion
Der Spezialfall für welchen die Fox H-Funktion zur Meijer G-Funktion reduziert wird ist bei Aj = Bk = C, C > 0 für j = 1...p und k = 1...q
Eine Verallgemeinerung der Fox H-Funktion ist geben von Ram Kishore Saxena[2] und Innayat Hussain AA (1987). Für eine weitere Verallgemeinerung, welche sich in der Physik und Statistik als nützlich erweisen wie A.M.Mathai und Ram Kishore Saxena zeigten,[3] siehe Rathie (1997).
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Pushpa Narayan and Luan Carlos de Sena Monteiro Rathie and Ozelim: On the Relation between Lambert W-Function and Generalized Hypergeometric Functions. In: Researchgate. Abgerufen am 1. März 2023.
- ↑ ISBN 978-0-387-06482-6 (englisch).
- ↑ ISBN 978-0-470-26380-8 (englisch).
![{\displaystyle H_{p,q}^{\,m,n}\!\left[z\left|{\begin{matrix}(a_{1},A_{1})&(a_{2},A_{2})&\ldots &(a_{p},A_{p})\\(b_{1},B_{1})&(b_{2},B_{2})&\ldots &(b_{q},B_{q})\end{matrix}}\right.\right]={\frac {1}{2\pi i}}\int _{L}{\frac {\prod _{j=1}^{m}\Gamma (b_{j}+B_{j}s)\,\prod _{j=1}^{n}\Gamma (1-a_{j}-A_{j}s)}{\prod _{j=m+1}^{q}\Gamma (1-b_{j}-B_{j}s)\,\prod _{j=n+1}^{p}\Gamma (a_{j}+A_{j}s)}}z^{-s}\,ds,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c1e0af72e03a0f3221f7f5241446802e999ff5b4)
![{\displaystyle {\overline {\operatorname {W} _{-1}\left(-\alpha \cdot z\right)}}={\begin{cases}\lim _{\beta \to \alpha ^{-}}\left[{\frac {\alpha ^{2}\cdot \left(\left(\alpha -\beta \right)\cdot z\right)^{\frac {\alpha }{\beta }}}{\beta }}\cdot \operatorname {H} _{1,\,2}^{1,\,1}\left({\begin{matrix}\left({\frac {\alpha +\beta }{\beta }},\,{\frac {\alpha }{\beta }}\right)\\\left(0,\,1\right),\,\left(-{\frac {\alpha }{\beta }},\,{\frac {\alpha -\beta }{\beta }}\right)\\\end{matrix}}\mid -\left(\left(\alpha -\beta \right)\cdot z\right)^{{\frac {\alpha }{\beta }}-1}\right)\right],\,{\text{falls}}\left|z\right|<{\frac {1}{e\left|\alpha \right|}}\\\lim _{\beta \to \alpha ^{-}}\left[{\frac {\alpha ^{2}\cdot \left(\left(\alpha -\beta \right)\cdot z\right)^{-{\frac {\alpha }{\beta }}}}{\beta }}\cdot \operatorname {H} _{2,\,1}^{1,\,1}\left({\begin{matrix}\left(1,\,1\right),\,\left({\frac {\beta -\alpha }{\beta }},\,{\frac {\alpha -\beta }{\beta }}\right)\\\left(-{\frac {\alpha }{\beta }},\,{\frac {\alpha }{\beta }}\right)\\\end{matrix}}\mid -\left(\left(\alpha -\beta \right)\cdot z\right)^{1-{\frac {\alpha }{\beta }}}\right)\right],\,{\text{andernfalls}}\\\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/68f1300bcfd5a4d55c52ae6c3c6c849d643f4f8e)



![{\displaystyle H_{p,q}^{\,m,n}\!\left[z\left|{\begin{matrix}(a_{1},C)&(a_{2},C)&\ldots &(a_{p},C)\\(b_{1},C)&(b_{2},C)&\ldots &(b_{q},C)\end{matrix}}\right.\right]={\frac {1}{C}}G_{p,q}^{\,m,n}\!\left(\left.{\begin{matrix}a_{1},\dots ,a_{p}\\b_{1},\dots ,b_{q}\end{matrix}}\;\right|\,z^{1/C}\right).}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8a258456f0dee32c310e13948bff8e3c8f4bb2de)