Benutzer:Paulgerhard/Chirale Alkohole
Chirale Alkohole[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Die beiden Enantiomere eines chiralen Moleküls unterscheiden sich räumlich voneinander im Aufbau, ähnlich wie rechte und linke Hand. Enantiomere verhalten sich wie Bild und Spiegelbild. Die isomeren Moleküle können durch Drehung nicht zur Deckung gebracht werden. Die beiden Enantiomere unterscheiden sich in den meisten physikalischen und chemischen Eigenschaften nicht. Sie besitzen gleiche Schmelzpunkte- und Siedepunkte, die gleiche Dichte und gehen (mit nicht-chiralen Reaktionspartnern) die gleichen Reaktionen mit den identischen Geschwindigkeits- und Gleichgewichts-Konstanten ein. Die einzige physikalische Eigenschaft, in der sich die Enantiomere unterscheiden, ist die Optische Aktivität. Unterschiede gibt es aber in der Reaktivität mit anderen chiralen Verbindungen. Besonders deutlich wird dies bei enzymkatalysierten Reaktionen. Die meisten Enzyme setzen nur eines der Enantiomere um, das andere Isomer bleibt unverändert.[1]
Chirale Mono-Alkohole[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
| Chemische Gruppe | Summenformel | Molare Masse g·mol−1 | Strukturformel | Chirale-Verbindung | Andere Namen | CAS-Nummer | PubChem Nummer
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propanole | C4H10O2 | 90,12 g·mol−1 | 
|
1-Methoxy-2-propanol[2] |
|
|
|
| Butanole | C4H10O | 74,12 g·mol−1 | 
|
2-Butanol[2] |
|
|
|
| Pentanole | C5H12O | 88,15 g·mol−1 | 
|
2-Pentanol[2] |
|
|
|
| C5H12O | 88,15 g·mol−1 | 
|
2-Methyl-1-butanol[2] |
|
|
| |
| C5H12O | 88,15 g·mol−1 | 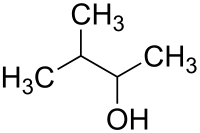
|
3-Methyl-2-butanol[2] |
|
|
| |
| Hexanole | C6H13O | 102,18 g·mol−1 | Es gibt 17 Strukturisomere | Hexanol[2] |
|
| |
| Octanole | C8H18O | 130,23 g·mol−1 | 
|
2-Octanol[2] |
|
|
|
| C8H18O | 102,18 g·mol−1 | 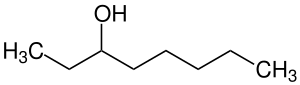
|
3-Octanol[2] |
|
|
| |
| C8H18O | 130,23 g·mol−1 | 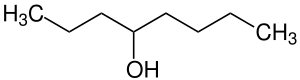
|
4-Octanol[2] |
|
|
| |
| Octenole | C8H16O | 128,22 g·mol−1 | 
|
1-Octen-3-ol[2] |
|
| |
| C8H16O | 128,21 g·mol−1 | 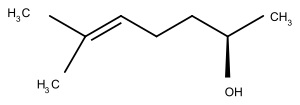
|
6-Methyl-5-Hepten-2-ol[3] |
|
|
| |
| Nonanole | C9H20O | 144,26 g·mol−1 | 
|
4-Nonanol[2] |
|
|
|
| Decanole | C10H22O | 158,29 g·mol−1 | 
|
2-Decanol[2] | Methyloctylcarbinol
|
|
|
| C10H22O | 158,29 g·mol−1 | 
|
3-Decanol[2] |
|
|
| |
| C10H22O | 158,29 g·mol−1 | 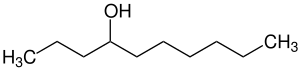
|
4-Decanol[2] |
|
|
| |
| C10H22O | 158,28 g·mol−1 | 
|
5-Decanol[2] |
|
|
|
Chirale-Diole[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
| Chemische Gruppe | Summenformel | Molare Masse g·mol−1 | Strukturformel | Chirale-Verbindung | Andere Namen | CAS-Nummer | PubChem Nummer
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propandiole | C3H8O2 | 76,09 g·mol−1 | 
|
1,2-Propandiol[2] |
|
|
|
| Butandiole | C4H10O2 | 90,12 g·mol−1 | 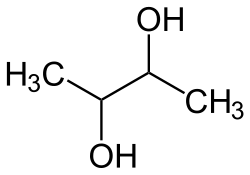
|
2,3-Butandiol[2] |
|
|
|
| Pentandiole | C5H12O2 | 104,15 g·mol−1 | 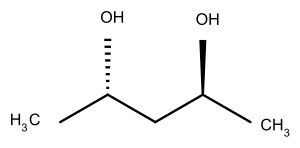
|
2,4-Pentandiol[3] |
|
|
|
| Hexandiol | C6H14O2 | 118,18 g·mol−1 | 
|
2,5-Hexandiol[3] |
|
|
|
| Heptandiol | C7H16O2 | 132,20 g·mol−1 | 
|
3,5-Heptandiol[3] |
|
|
|
| Octandiol | C8H18O2 | 146,23 g·mol−1 | 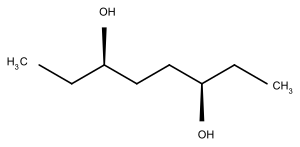
|
3,6-Octandiol[3] |
|
|
|
Chirale Hydroxyester[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
| Chemische Gruppe | Summenformel | Molare Masse g·mol−1 | Strukturformel | Chirale-Verbindung | Andere Namen | CAS-Nummer | PubChem Nummer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methyl-3-Hydroxybutyrate | C5H10O3 | 118,13 g·mol−1 | 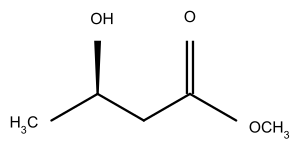
|
Methyl-3-Hydroxybutyrat[3] |
|
|
|
| Ethyl-3-Hydroxybutyrate | C6H12O3 | 132,159 g·mol−1 | 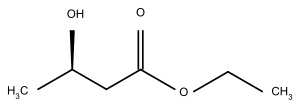
|
Ethyl-3-Hydroxybutyrat[3] |
|
|
|